Introduction:
Being attuned to your pet’s behavior is key to fostering a harmonious and fulfilling relationship. Understanding the signals and cues your furry friend communicates can enhance the bond between pet parents and their companions. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of pet behavior, providing insights and tips for pet parents to decode and respond to their pets’ actions effectively.
Section 1: Canine Communication
1.1. Body Language: Dogs communicate primarily through body language. Understanding cues such as wagging tails, raised hackles, or relaxed ears can offer insights into your dog’s emotional state. For example, a wagging tail may indicate excitement, while a tucked tail suggests fear or anxiety.
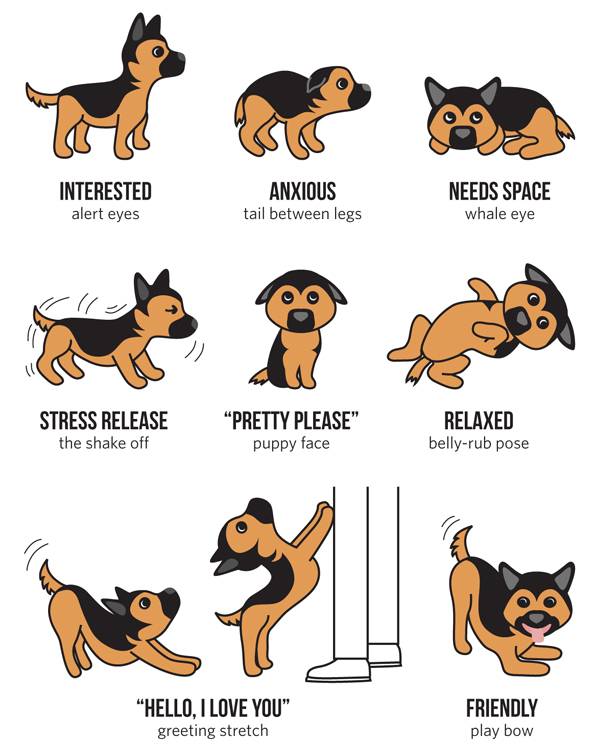
1.2. Vocalizations: Dogs use a variety of vocalizations to express themselves. Barking, whining, growling, and howling are all forms of communication. Pay attention to the pitch, volume, and context to interpret what your dog is trying to convey.
Section 2: Feline Expressions
2.1. Tail Language: Cats use their tails to communicate a range of emotions. A raised tail indicates happiness, while a puffed-up tail suggests fear or agitation. A slow tail flick may signify annoyance, and a tucked tail could signal anxiety.
2.2. Purring: While commonly associated with contentment, cats may purr for various reasons, including stress or illness. Pay attention to accompanying behaviors and the context to determine the meaning behind your cat’s purring.
Section 3: Environmental Responses
3.1. Territorial Marking: Both dogs and cats have a strong sense of territory. Scratching, rubbing against objects, or urine marking are ways pets establish and mark their territory. Provide designated spaces for such behaviors to maintain a balanced environment.
3.2. Stress Indicators: Changes in behavior, such as excessive grooming, hiding, or loss of appetite, may indicate stress in pets. Recognizing these signs early allows pet parents to address and alleviate potential stressors.
Section 4: Training and Reinforcement
4.1. Positive Reinforcement: Positive reinforcement is a powerful tool in shaping desirable behaviors. Reward your pet with treats, praise, or play when they exhibit positive actions. This encourages them to repeat those behaviors.:strip_icc()/GettyImages-1164933752-c635f6c4f96047ea8e562d0c0a0d3611.jpg)
4.2. Consistency in Training: Consistency is key when training pets. Set clear rules and boundaries, and ensure all family members follow them. This provides a stable environment, reducing confusion and stress for your pets.
Section 5: Seeking Professional Guidance
5.1. Behavioral Challenges: If you encounter persistent behavioral challenges, seeking professional guidance from a veterinarian or animal behaviorist is essential. They can assess underlying issues and provide tailored solutions to address specific behaviors.
5.2. Training Classes: Enrolling in training classes or seeking the assistance of a certified trainer can be beneficial. These classes not only teach essential commands but also provide socialization opportunities for your pet.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding pet behavior is an ongoing process that requires observation, patience, and empathy. By decoding your pet’s cues and responding appropriately, you’ll build a stronger and more enriching relationship with your furry companion. Remember, each pet is unique, and the key to effective communication lies in recognizing their individual personalities and needs. Armed with this guide, pet parents can embark on a journey of mutual understanding and companionship with their beloved pets.